Python Basics Tutorial — एक आसान और दिलचस्प शुरुआत
🔹 1. Python क्या है?
Python एक high-level programming language है, मतलब कि आपको ज़्यादा technical syntax की चिंता नहीं करनी पड़ती।
आप simple English जैसे code लिख सकते हैं।
इसी वजह से इसे beginner-friendly language कहा जाता है।
print("Hello, World!")बस इतना लिखो — और Python आपको "Hello, World!" दिखा देगा।
कितना आसान है ना?
🔹 2. Python क्यों सीखें?
- 📘 आसान syntax — पढ़ने और समझने में simple
- ⚙️ Powerful — web apps, data science, AI, machine learning, automation सब में use होता है।
- 🌍 Huge community — लाखों लोगों की help और ready-made libraries
- 💼 Career scope — हर tech field में Python developer की demand है।
🔹 3. Python कैसे install करें?
- python.org पर जाएँ
- Latest version download करें (Windows, Mac, Linux सभी के लिए available है।)
- Install करते समय "Add Python to PATH" option जरूर tick करें ✅
अब command prompt (या terminal) खोलकर लिखें:
python --version
अगर version दिखे, तो Python तैयार है!
🔹 4. पहला प्रोग्राम
अब एक simple program बनाते हैं:
एक फाइल बनाइए — first.py
print("Python सीखना आसान है!")python first.py
Python सीखना आसान है!बधाई हो 🎉 — आपने अपना पहला Python प्रोग्राम लिखा।
🔹 5. Variables (डेटा स्टोर करने का तरीका)
Variable मतलब — नाम देकर कोई value रखना।
name = "Skill and Dedication"
age = 25
print(name)
print(age)
Skill and Dedication
25
👉 Python में data type बताने की ज़रूरत नहीं होती, वो खुद समझ लेता है।
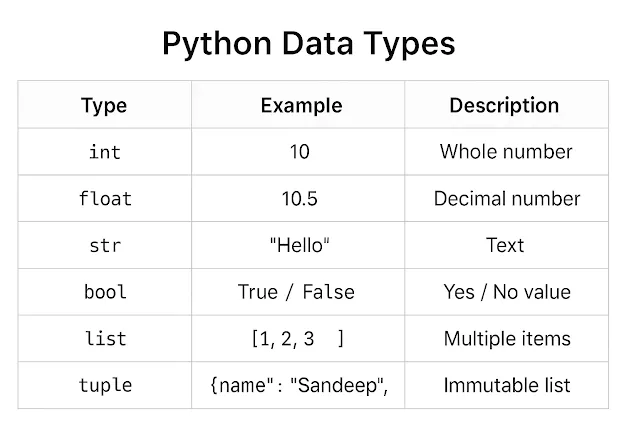
🔹 6. Data Types (डेटा के प्रकार)
| Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
int |
10 |
Whole number |
float |
10.5 |
Decimal number |
str |
"Hello" |
Text |
bool |
True / False |
Yes / No value |
list |
[1, 2, 3] |
Multiple items |
tuple |
(1, 2, 3) |
Immutable list |
dict |
{"name":"Sandeep", "age":25} |
Key-value pair |
🔹 8. Operators (गणितीय ऑपरेशन)
Operators क्या होते हैं?
Operators वो symbols होते हैं जिनसे हम variables और values पर operations करते हैं।
A) Arithmetic Operators
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | 5 + 3 | 8 |
| - | Subtraction | 5 - 3 | 2 |
| * | Multiplication | 5 * 3 | 15 |
| / | Division | 5 / 2 | 2.5 |
| // | Floor Division | 5 // 2 | 2 |
| % | Modulus | 5 % 2 | 1 |
| ** | Exponent | 5 ** 2 | 25 |
x = 10
y = 3
print(x + y) # 13
print(x // y) # 3
print(x ** y) # 1000
B) Comparison Operators
इनका उपयोग दो values की तुलना करने के लिए किया जाता है। Output हमेशा True या False होता है।
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equal To | 5 == 5 | True |
| != | Not Equal | 5 != 3 | True |
| > | Greater Than | 5 > 3 | True |
| < | Less Than | 3 < 5 | True |
| >= | Greater or Equal | 5 >= 5 | True |
| <= | Less or Equal | 3 <= 5 | True |
C) Logical Operators
Multiple conditions को check करने के लिए इस्तेमाल होते हैं।
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| and | Both True | True and False | False |
| or | Any True | True or False | True |
| not | Reverse | not True | False |
x = 5
y = 10
print(x > 3 and y > 5) # True
print(x > 3 or y < 5) # True
print(not(x > 3)) # False
D) Assignment Operators
| Operator | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|
| = | Assign | x = 5 |
| += | Add & Assign | x += 3 → x = x + 3 |
| -= | Subtract & Assign | x -= 2 → x = x - 2 |
| *= | Multiply & Assign | x *= 2 → x = x * 2 |
| /= | Divide & Assign | x /= 2 → x = x / 2 |
| **= | Exponent & Assign | x **= 2 → x = x ** 2 |
E) Membership Operators
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| in | Present | 'a' in 'apple' | True |
| not in | Not Present | 5 not in [1,2,3] | True |
F) Identity Operators
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| is | Same object | x is y | True/False |
| is not | Not same | x is not y | True/False |
🔹 9. Conditional Statements (अगर ऐसा है तो...)(Decision Making)
इनका उपयोग किसी condition के आधार पर अलग-अलग code चलाने के लिए किया जाता है।
A) if Statement
age = 18
if age >= 18:
print("You are an adult")
B) if-else Statement
age = 15
if age >= 18:
print("Adult")
else:
print("Minor")
C) if-elif-else Statement
marks = 85
if marks >= 90:
print("Grade A")
elif marks >= 70:
print("Grade B")
else:
print("Grade C")
D) Nested if
age = 20
marks = 75
if age >= 18:
if marks >= 80:
print("Adult with good marks")
else:
print("Adult with average marks")
else:
print("Minor")
E) Short Hand If (Ternary Operator)
age = 18
print("Adult") if age >= 18 else print("Minor")
💡 निष्कर्ष:
Operators और Conditional Statements, Python प्रोग्रामिंग के सबसे जरूरी हिस्से हैं।
इनसे आप logic बना सकते हैं, data compare कर सकते हैं और program का flow control कर सकते हैं।
🔹 10. Loops (बार-बार काम करना)
Loop का मतलब होता है किसी काम को बार-बार दोहराना। Python में दो मुख्य लूप होते हैं — for loop और while loop।
1️⃣ for Loop
for loop का इस्तेमाल किसी sequence (जैसे list, string या range) पर iterate करने के लिए किया जाता है।
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "mango"]
for item in fruits:
print(item)
for loop with range()
for i in range(1, 6):
print(i)
Nested for Loop
for i in range(1, 4):
for j in range(1, 3):
print(i, j)
2️⃣ while Loop
जब तक condition True रहती है, loop चलता रहता है।
i = 1
while i <= 5:
print(i)
i += 1
3️⃣ Loop Control Statements
| Keyword | Meaning | Use |
|---|---|---|
| break | Loop रोक देता है | जब condition पूरी हो जाए |
| continue | Current iteration skip | कुछ values skip करने के लिए |
| pass | कुछ नहीं करता | Placeholder के रूप में |
break Example
for i in range(1, 10):
if i == 5:
break
print(i)
continue Example
for i in range(1, 6):
if i == 3:
continue
print(i)
pass Example
for i in range(1, 5):
if i == 3:
pass
print(i)
else with Loop
for i in range(1, 4):
print(i)
else:
print("Loop completed successfully!")
💡 निष्कर्ष:
Python में loops आपको repetitive tasks को automate करने की सुविधा देते हैं। आप loops के साथ break, continue, pass और else का इस्तेमाल करके complex logic भी बना सकते हैं।
Python में loops आपको repetitive tasks को automate करने की सुविधा देते हैं। आप loops के साथ break, continue, pass और else का इस्तेमाल करके complex logic भी बना सकते हैं।
🔹 11. Functions (बार-बार उपयोग होने वाला कोड)
def greet(name):
print("नमस्ते,", name)
greet("Skill and Dedication")
greet("Python Learner")
नमस्ते, Skill and Dedication
नमस्ते, Python Learner🔹 12. List (एक साथ कई वैल्यू)
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "mango"]
print(fruits[0]) # पहला आइटम
fruits.append("orange") # नया जोड़ें
print(fruits)
apple
['apple', 'banana', 'mango', 'orange']
🔹 13. Dictionary (Key:Value फॉर्मेट)
student = {
"name": "Skill and Dedication",
"age": 21,
"course": "Python"
}
print(student["name"])
print(student.get("course"))
Output:
Skill and Dedication
Python
🔹 14. File Handling (फाइल में पढ़ना-लिखना)
# लिखना
with open("data.txt", "w") as f:
f.write("Hello Python!")
# पढ़ना
with open("data.txt", "r") as f:
print(f.read())
Output:
Hello Python!
🔹 14. Python से क्या बना सकते हैं? 🚀
Python एक ऐसी भाषा है जिससे लगभग कुछ भी बनाया जा सकता है।
यहाँ कुछ उदाहरण हैं 👇
यहाँ कुछ उदाहरण हैं 👇
| क्षेत्र | क्या बना सकते हैं | उपयोगी टूल / लाइब्रेरी |
|---|---|---|
| 🌐 वेब डेवलपमेंट | वेबसाइट, ब्लॉग, पोर्टफोलियो | Django, Flask, FastAPI |
| 🤖 AI और Machine Learning | चैटबॉट, फेस रिकग्निशन, प्रेडिक्शन सिस्टम | TensorFlow, PyTorch |
| 📊 डेटा साइंस | रिपोर्ट्स, चार्ट, डेटा एनालिसिस | Pandas, Matplotlib, NumPy |
| ⚙️ ऑटोमेशन | रोज़ के काम ऑटोमेट करना (ईमेल भेजना, फाइल रीनेम) | Selenium, PyAutoGUI |
| 📱 मोबाइल ऐप्स | Android / iOS ऐप्स | Kivy, BeeWare |
| 💻 डेस्कटॉप सॉफ्टवेयर | टूल्स जैसे नोटपैड, कैलकुलेटर | Tkinter, PyQt |
| 🎮 गेम डेवलपमेंट | 2D गेम्स, इंटरएक्टिव गेम्स | Pygame |
| 🔐 साइबर सिक्योरिटी टूल्स | नेटवर्क स्कैनर, पासवर्ड टूल्स | Scapy, Nmap-python |
| 💬 चैटबॉट और ऑटो रिप्लाई सिस्टम | Telegram या AI Bot | ChatterBot, openai |
16. निष्कर्ष (Conclusion)
- Python एक बहुत आसान और ताकतवर भाषा है।
- थोड़ा रोज़ अभ्यास करो, छोटे-छोटे प्रोजेक्ट बनाओ, और कोड से खेलो।
- धीरे-धीरे आप खुद देखोगे कि Python आपके लिए कितनी मज़ेदार और फायदेमंद है।